In this course we looked into various learning theories (behaviourism, cognitivism, constructivism, social learning, connectivism) within the context of teaching. When asked to describe my own teaching practices and subsequent student learning within these theories, and my belief around how learning takes place, I should first describe or define what each of these learning theories are.
- Behaviourism in teaching focuses on observable behaviours as the primary study, suggesting that learning occurs through conditioning, where students respond to stimuli in their environment, forming associations between stimuli and responses, with reinforcement and punishment influencing behaviour repetition.
- Cognitivism highlights the role of mental processes in teaching, emphasizing memory, thinking, and problem-solving. This theory believes that learners actively process information, organize knowledge, and create mental representations to understand and solve problems, stressing the importance of internal cognitive structures.
- Constructivism suggests that learners actively construct their understanding of the world by engaging with experiences and integrating new knowledge with existing mental structures, emphasizing the role of social and cultural context in shaping learning experiences.
- Social Learning Theory in the educational context underscores the importance of observation and modelling, proposing that students learn by observing others’ behaviours and their consequences, involving the acquisition of new behaviours through imitation, reinforcement, and social interactions.
- Connectivism, relevant to teaching, acknowledges the impact of technology and the interconnected nature of information in the digital age. It proposes that learning occurs through networked connections, where students access and share information in distributed environments, emphasizing the need to stay connected to diverse sources and adapt to the changing educational landscape.
Reflecting on my practices primarily as a woodwork teacher, I believe there are examples of student learning and best practices within all of these learning theories. Here are some examples of best practices I use for each of these main learning theories.
- I use a behaviourist approach through using positive reinforcement, such as praising a student for using proper safety procedures while operating machinery. The reinforcement strengthens the association between safe behaviour and positive outcomes, encouraging the student to consistently follow safety guidelines when working on their projects.
- I use a cognitivist approach by focusing on the mental processes involved in problem-solving. For instance, I have students mentally plan and visualize the steps required to create their project, considering measurements, tools, machinery, and assembly sequences before actually beginning their projects.
- I use a constructivist approach through hands-on experiences and interactions with materials. Students actively construct their understanding of woodworking concepts, drawing on prior knowledge from previous projects or demonstrations, and adapting their approaches to new projects.
- I use a social learning approach as students observe and learn from their peers. Students observe other classmates safely using a specific woodworking technique or tool, and are subsequently encouraged to use that technique or tool they just observed into their own projects. A shared knowledge within the group, and an observation of other students completing their projects, often also results in encouragement to continue working on their own projects.
- I use (or rather plan to use more of) a connectivism approach as I have recently started converting my old handouts into digital formats so students can access these and other tutorials, digital textbooks, YouTube videos and more online. I plan on creating a new localized digital platform to share and discuss plans, techniques, resources, and projects with a broader community of Tech Ed / ADST teachers and our students. The emphasis will be on networked learning, where students connect with diverse sources of information beyond the traditional setting of my woodshop.
I believe that learning takes place within all of these theories to varying degrees based on the topic at hand, and the specific learners. I tend to use a mixed methods approach of learning theories to my lessons as I see merit in all approaches. If I had to pick one over another however, I would say that the hands-on nature of being in the woodshop lends itself more towards a constructivist approach to learning.
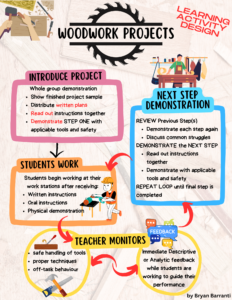
Furthermore, when looking at learning theories for any subject area, or specific lesson within, teachers need to also understand the various learning styles of all of their students. I tend to use a more Universal Designs for Learning (UDL) approach to my lessons aiming to provide a variety of instructional approaches to accommodate the diverse learning preferences of my students and create a more inclusive learning environment in my shop/classroom. An example of a typical Learning Design Activity of mine in the Woodshop would be as illustrated below.
Key points:
- INTRODUCE PROJECT Whole group demonstration to introduce the project. I show an example of a finished project as a means to inform students of the objectives. I provide written plans (for reading/writing learners) so students can read on their own if preferred or needed as a reference, I read out loud (for auditory learners) the instructions together for each step, and then I demonstrate (for visual learners) the first step with the applicable tools and safety concerns addressed.
- STUDENTS WORK Students begin hands-on working (for kinesthetic learners) on their projects after receiving the written instructions, oral instructions, and physical demonstration. This is done to elicit performance as students apply what they have learned to reinforce new skills and knowledge.
- TEACHER MONITORS I then circulate to ensure safe handling of tools, proper tool or machinery techniques are being used, and to limit the off-task behaviours of students. During this time I also provide immediate Descriptive/Analytic Feedback while students are working to facilitate their learning towards safe execution and success.
- REVIEW AND NEXT STEP DEMONSTRATIONS I then pull the class together again to review the previous step through talking about and demonstrating the step again as a means to stimulate recall of prior learning. I also further discuss common struggles that students encountered and provide more tips. I then read out loud the next step and physically demonstrate the next step in the same manner as before.
- LOOPING BEGINS: REPEAT LEARNING ACTIVITY We then continue the looping cycle of Students Work — Teacher Monitors — Review Previous Steps and Demonstrate Next Step until the final step is completed. This continuous review of steps 1–2, then 1–3, then 1–4, etc ensures all students are receiving relevant and timely instruction no matter their pace of learning.